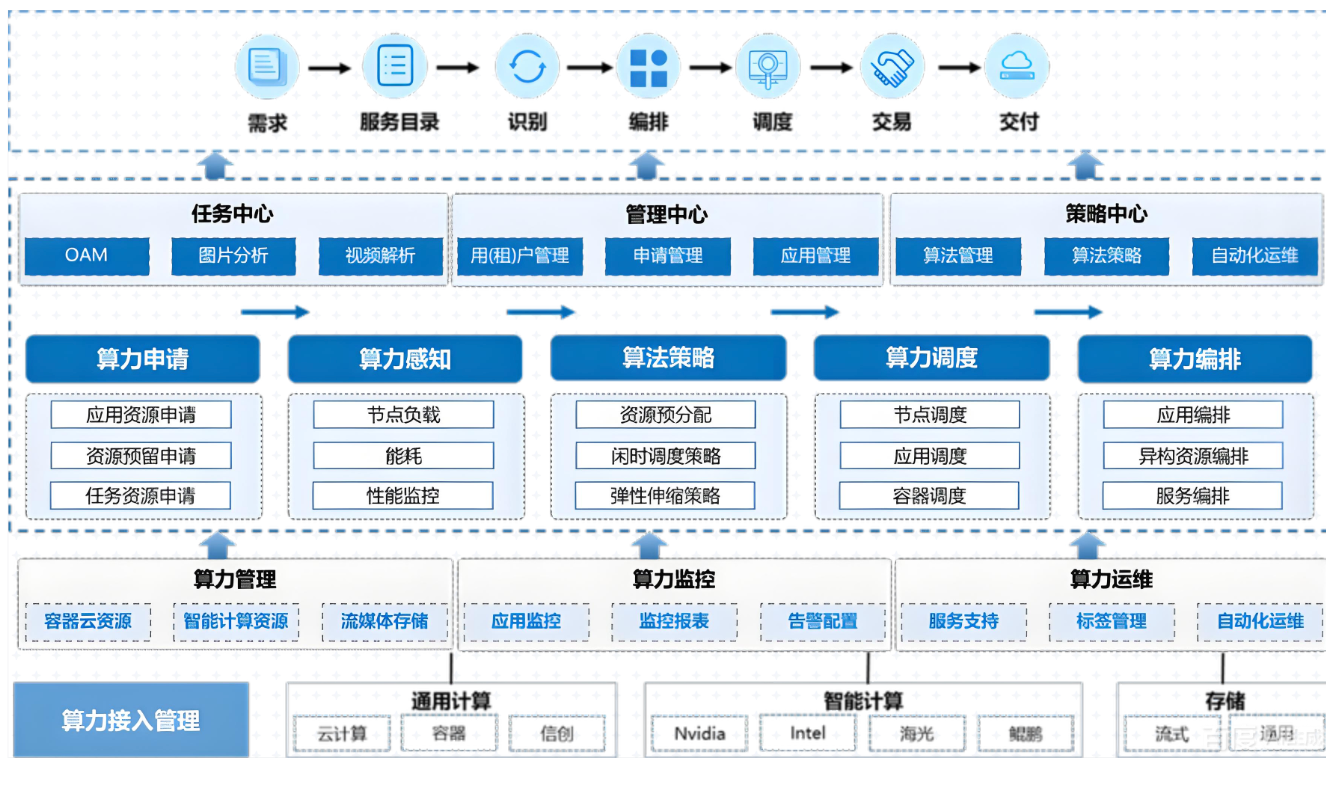
 In today's rapidly evolving new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation, the deep integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming a key engine driving high-quality social development. As a representative of cutting-edge technology, the edge AI sensing platform launched by Dishan Technology not only demonstrates excellent performance in intelligent perception, real-time decision-making, and low latency response, but also plays an increasingly important role in talent cultivation. This platform provides strong support for the growth of compound and innovative scientific and technological talents in the new era by building an integrated education ecosystem of "theory practice innovation". Its core value lies not only in technological empowerment, but also in delivering "future engineers" with practical skills and innovative thinking to the industry through multidimensional educational innovation.
In today's rapidly evolving new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation, the deep integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming a key engine driving high-quality social development. As a representative of cutting-edge technology, the edge AI sensing platform launched by Dishan Technology not only demonstrates excellent performance in intelligent perception, real-time decision-making, and low latency response, but also plays an increasingly important role in talent cultivation. This platform provides strong support for the growth of compound and innovative scientific and technological talents in the new era by building an integrated education ecosystem of "theory practice innovation". Its core value lies not only in technological empowerment, but also in delivering "future engineers" with practical skills and innovative thinking to the industry through multidimensional educational innovation.
Building real-life scenarios and strengthening practical ability cultivation: "practical exercises" from the laboratory to the front line of the industry
In traditional education models, students often face the dilemma of "disconnection between learning and application", especially in highly application-oriented fields such as AI and sensor technology. Dishan Technology’s Edge AI Sensing Platform integrates high-precision sensors, edge computing units and AI algorithms, capable of simulating dozens of real-world application scenarios including smart cities, industrial automation, smart agriculture and environmental monitoring.
Colleges, universities and research institutions can build experimental systems based on this platform, enabling students to gain hands-on experience throughout the entire process of real data collection, model training, edge deployment and system optimization—thus significantly enhancing their engineering practical capabilities.
For instance, in the smart city simulation scenario, students can use the platform to collect real-time data such as traffic flow, air quality and noise pollution, and leverage edge-side AI models to conduct congestion early warning and pollution source tracing analysis. In the industrial automation scenario, the platform supports real-time monitoring of parameters such as vibration, temperature and energy consumption of production line equipment, realizing early warning of equipment failures through anomaly detection models.
This closed-loop training of "from data to decision-making" allows students to deeply understand the full-link challenges of AI implementation. Every stage—from sensor selection and deployment, data cleaning and annotation, to algorithm tuning, edge computing resource allocation, and finally to system deployment and operation and maintenance—requires comprehensive consideration of technology, cost and feasibility.
In practical applications, an intelligent transportation system project was developed based on Dishan Technology’s platform. In this project, students achieved accurate prediction of urban traffic flow and applied the prediction results to the optimization of actual traffic signal lights, successfully reducing the congestion rate of roads around the campus.
Another student who participated in an industrial automation project reported that through learning and practice on the platform, he not only mastered equipment failure early warning technology, but also greatly improved his ability to solve practical engineering problems.
The platform also supports dynamic switching between multiple scenarios, allowing students to flexibly configure hardware modules and algorithm models according to the needs of different projects, thus fostering flexibility and systematic thinking to address complex engineering issues.
Lowering Technical Barriers to Unleash Innovation Potential: Making AI Development Accessible to All
Promoting interdisciplinary integration and cultivating versatile talents: breaking down disciplinary barriers and building a systematic understanding of "technology+scenarios"
The extensive application scenarios of Dishan Technology's Edge AI Sensing Platform are inherently interdisciplinary by nature. In smart agriculture, it is necessary to integrate agronomic knowledge, soil environment data and sensor data analysis; in intelligent healthcare, it requires the combination of biomedical signal processing, AI diagnostic algorithms and wearable device design; in smart manufacturing, it involves mechanical engineering, automatic control and industrial big data analysis.
When using the platform, students are compelled to break free from single-discipline thinking and take the initiative to acquire knowledge across multiple fields. For example, in the field of intelligent healthcare, students collaborated to develop a real-time health monitoring system based on the platform, which integrated biomedical signal processing technology and AI algorithms, successfully achieving accurate monitoring and anomaly early warning of patients' key health indicators. In smart agriculture, they developed an intelligent irrigation system using the platform, which integrated soil environment data and sensor analysis, effectively improving crop yield and quality.
Colleges and universities can leverage this platform to offer interdisciplinary courses or establish joint laboratories, facilitating collaborative efforts among students majoring in computer science, electronics, automation, environmental science, medicine and other disciplines. In the "Smart Greenhouse Project", agronomy students were responsible for analyzing crop growth indicators, electronic engineering students designed sensor nodes and wireless transmission networks, and computer science students built AI models to predict pest and disease risks. The interdisciplinary team worked together to complete the entire process from scheme design to system deployment.
This Project-Based Learning (PBL) model not only enhances students' teamwork and communication skills, but also cultivates their systematic problem-solving capabilities—from defining requirements and selecting technologies to implementing engineering solutions. It fully meets the urgent demand of future society for "T-shaped talents" (individuals who possess both in-depth professional expertise and broad interdisciplinary vision).
Supporting educational equity and expanding the breadth of talent cultivation: inclusive technology, allowing high-quality resources to benefit more students
The platform supports cloud-based management and remote access, enabling universities and colleges in remote areas to share high-quality technical resources.
Through the online experiment platform and virtual simulation system, students can participate in high-level AI practical teaching without the need for expensive hardware. For example, a university in western China leveraged the platform’s cloud lab to allow students to complete an intelligent traffic signal optimization project in a virtual environment, and finish code debugging and model deployment through remote collaboration.
Dishan Technology also regularly organizes technical training sessions, open-source projects and competitions, providing a platform for learning and showcasing talents to more aspiring young people. It thus creates opportunities for more students to access cutting-edge technologies and stimulates their potential for technological innovation.
Towards the future: building a sustainable talent cultivation ecosystem
With the continuous evolution of AIoT technology, the edge AI sensing platform of Dishan Technology is also constantly iterating and upgrading. In the future, the platform will deeply integrate cutting-edge technologies such as edge intelligence, digital twins, and federated learning, further expanding the complexity and authenticity of application scenarios; Develop more toolkits and course resources for new engineering education, supporting the "AI+X" interdisciplinary talent cultivation model; Deepening the mechanism of industry university research cooperation will continue to promote the construction of open source communities, bringing together various forces such as universities, enterprises, and developers to form an ecosystem of "co construction, sharing, and win-win", providing richer resources and a broader stage for talent cultivation.
